References
VSCode Extension
VS Code Extension
Introduction
Easily isolate your services from surrounding dependencies and write and run integration and performance tests as you develop and debug, directly in VSCode. Visit the VSCode extension marketplace to download and install the extension.
Getting Started
1. Set Up a Kubernetes Cluster
First, run the Set Up Cluster command to configure a Kubernetes cluster to use with Mocker and Tester.

Note: Please be aware that provisioning a local cluster is supported only on MacOS or Linux. On Windows, you can only connect to an existing cluster.
2. Deploy New Worker Container
Next, install the Worker container in your cluster by running the Deploy New Worker Container command.

Mocker
Mocker is an in-cluster solution for creating API mock servers. You can follow the following steps to use Mocker in the VS code extension:
1. Generate Mock
When you’re ready to mock a service, run the Generate Mock command to generate a mock configuration in the form of a .yaml file in the mocks folder of your working directory. You will be prompted to select an API schema file to mock against, and input some necessary configuration details including the Kubernetes service name, port number, and proto service name (if applicable).

Tip: We recommend running the generate command in your source code repo so mocks are versioned and shareable across your team.
2. Edit Mock
Mocker generates default values for responses based on the API signature. You can edit the default values by editing the generated mock in the mocks folder.

3. Apply Mock
Now, you can push the mock configuration to Mocker by running the Apply Mocks command:

That’s it! All calls to the mocked service/s are now routed to Mocker and it responds with the default values in the configuration.
Note: Mocker does not automatically update the mocks when the responses are updated in the mock configuration file. You can run the Apply Mocks command again when your mock values change. Note: When mocking a gRPC service the container needs to be redeployed if the proto definition of the mock changes.
Tester
How Tester works
Tester is a solution that simplifies the process of both writing and running tests for complicated distributed apps. You can follow the following steps to use Tester in the VS code extension:
1. Generate Test
When you’re ready to test a service, run the Generate Test command to generate a test configuration in the form of a .yaml file in the tests folder of your working directory. You will be prompted to select an API schema file to test against, and input some necessary configuration details including the test name, Kubernetes service name, port number, and proto service name (if applicable).

2. Edit Test
Tester generates default values for requests based on the API signature. You can edit the default values and add request steps by editing the generated test in the tests folder.

3. Start Test
Now, you can start the test configurations by running the Start Test command:
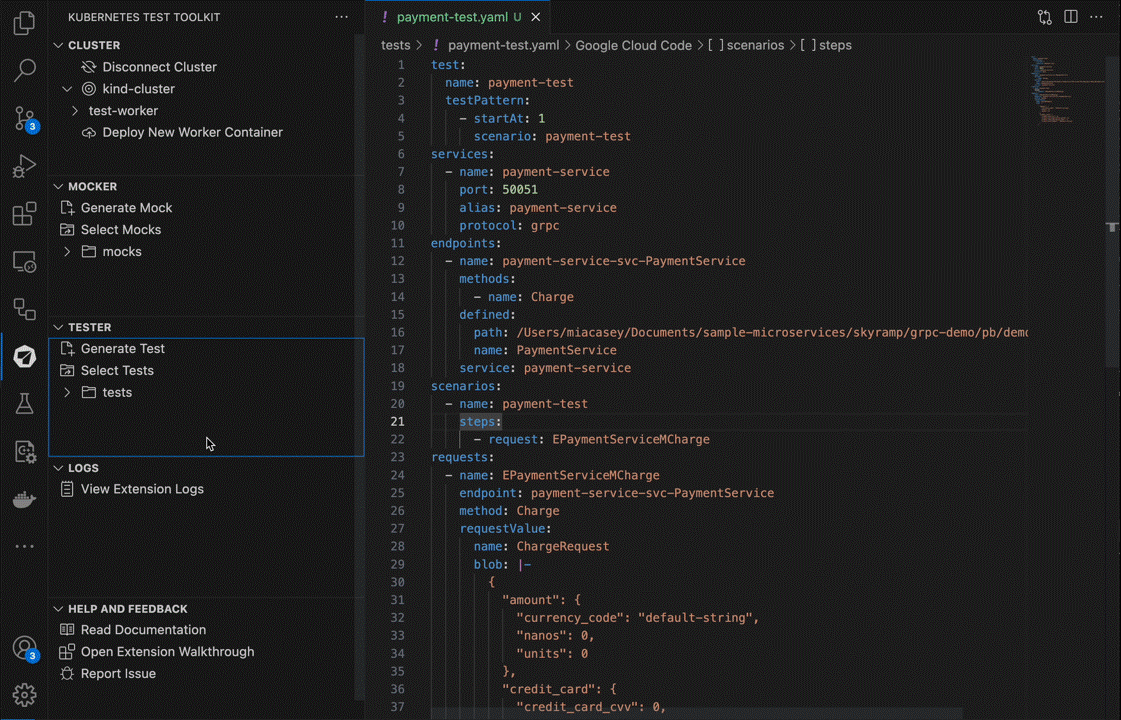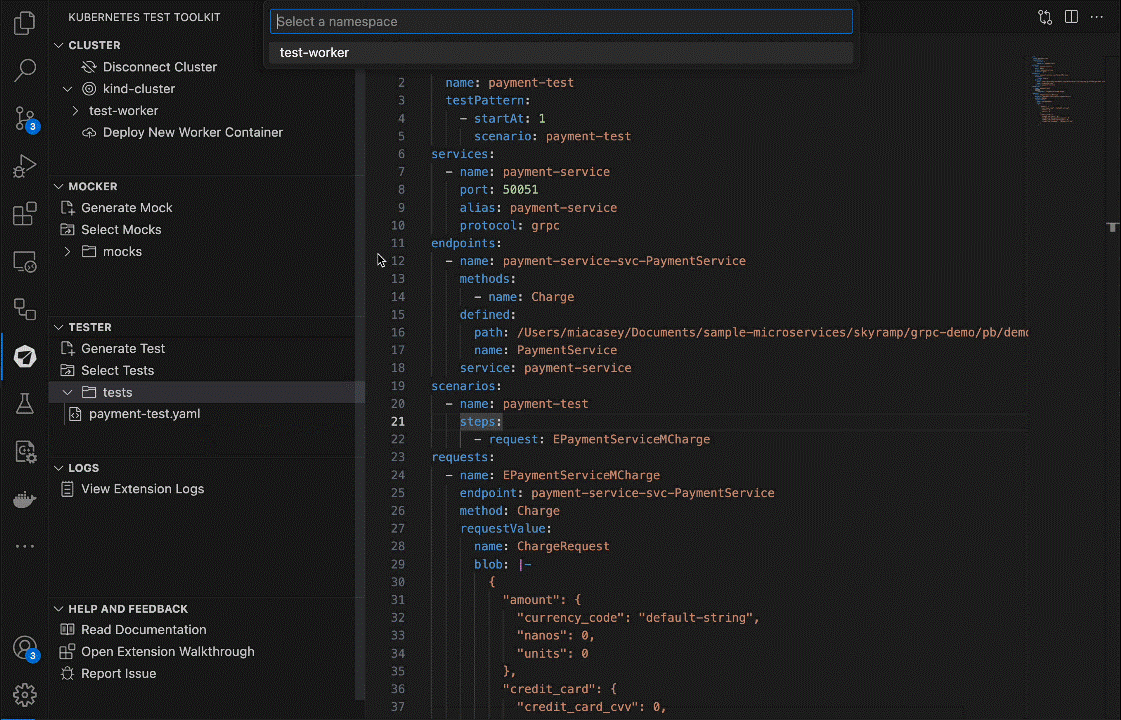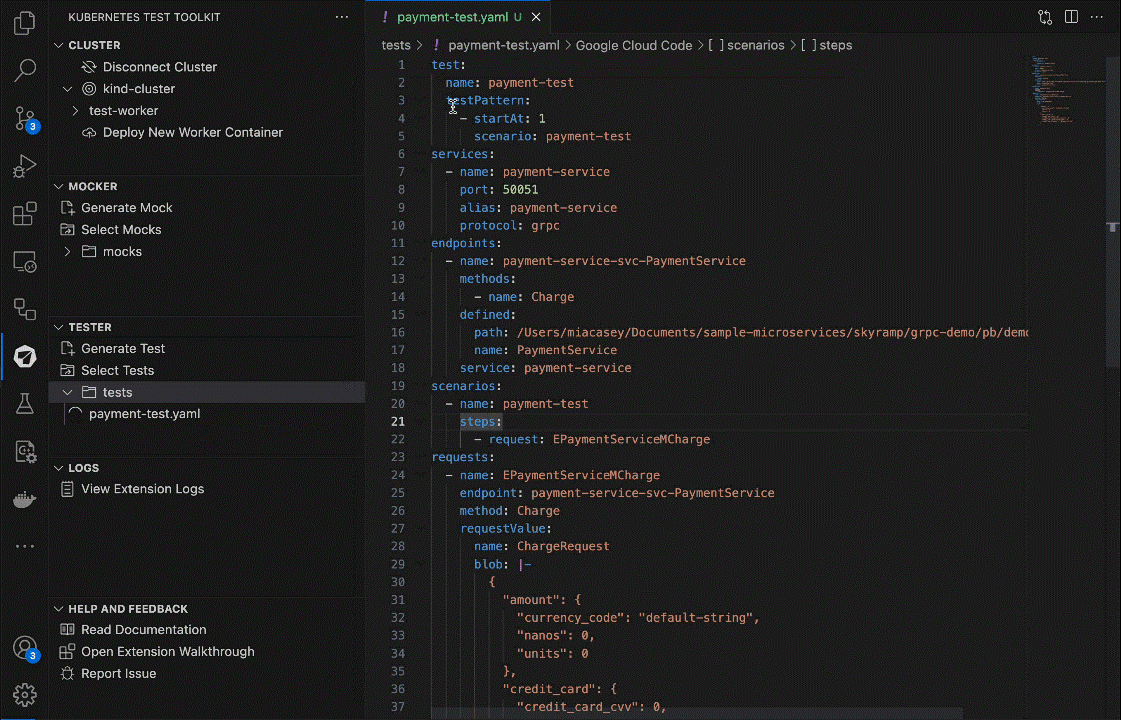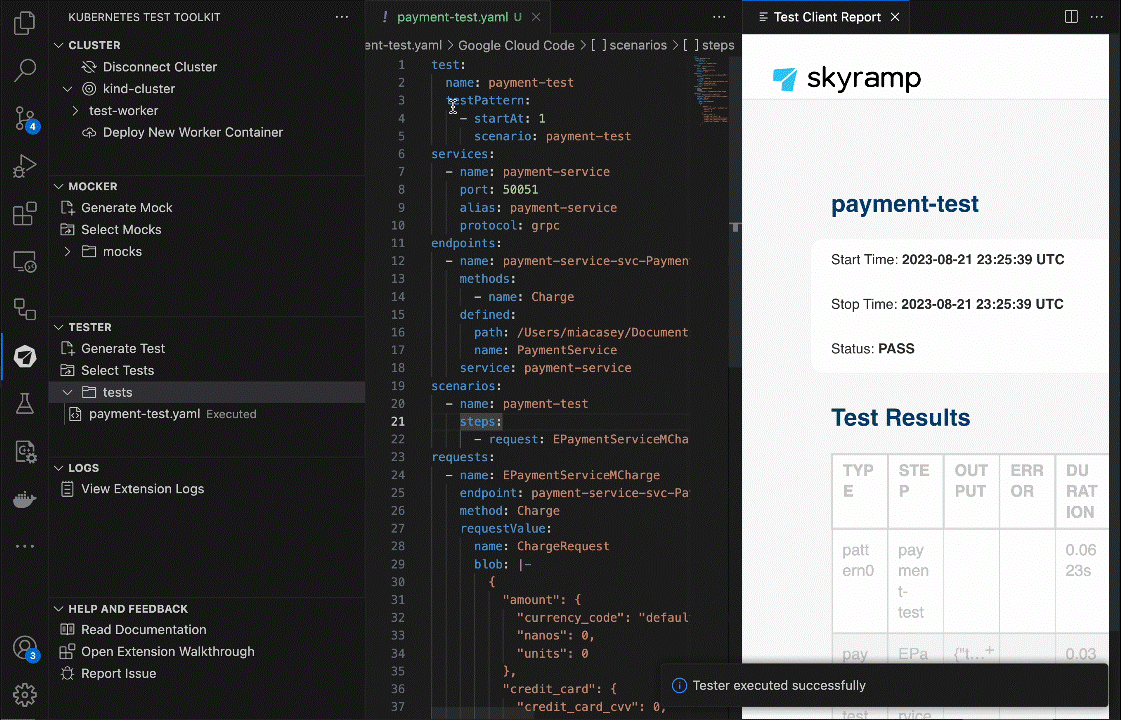
That’s it! Tester will execute the test and output on the test results in the results output directory.
Requirements
Helm
The Worker container is installed in your cluster via Helm. In case you don’t have Helm installed, refer to Helm’s documentation to get started.